Neutral style transfer
Neural Style Transfer (NST) refers to a class of software algorithms that manipulate digital images, or videos, to adopt the appearance or visual style of another image. NST algorithms are characterized by their use of deep neural networks in order to perform the image transformation. Common uses for NST are the creation of artificial artwork from photographs, for example by transferring the appearance of famous paintings to user supplied photographs. Several notable mobile apps use NST techniques for this purpose, including DeepArt and Prisma.

Pleriminary
NST is an example of image stylization, a problem studied for over two decades within the field of non-photorealistic rendering. Prior to NST, the transfer of image style was performed using machine learning techniques based on image analogy. Given a training pair of images–a photo and an artwork depicting that photo–a transformation could be learned and then applied to create a new artwork from a new photo, by analogy. The drawback of this method is that such a training pair rarely exists in practice. For example original source material (photos) are rarely available for famous artworks.
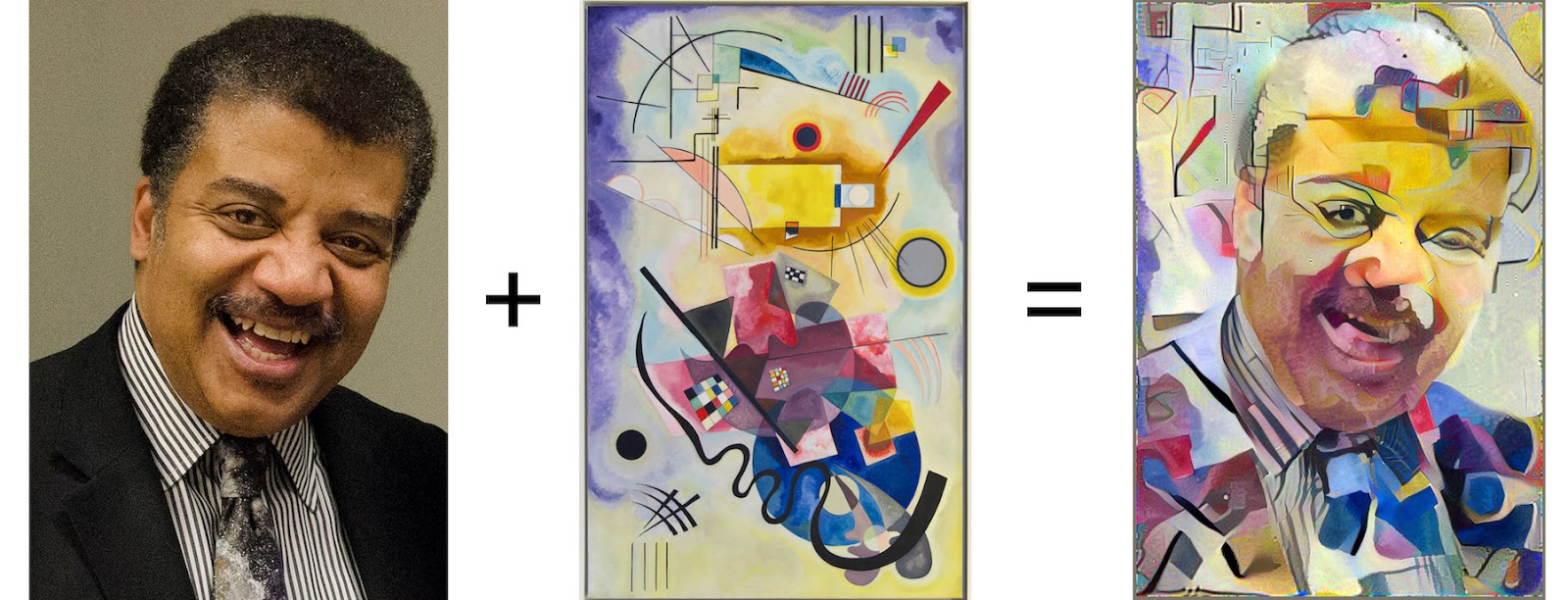
NST requires no such pairing; only a single example of artwork is needed for the algorithm to transfer its style.
