Linear regression
In statistics, linear regression is a linear approach to modeling the relationship between a scalar response (or dependent variable) and one or more explanatory variables (or independent variables). The case of one explanatory variable is called simple linear regression. For more than one explanatory variable, the process is called multiple linear regression. This term is distinct from multivariate linear regression, where multiple correlated dependent variables are predicted, rather than a single scalar variable.

Preliminary
In linear regression, the relationships are modeled using linear predictor functions whose unknown model parameters are estimated from the data. Such models are called linear models. Most commonly, the conditional mean of the response given the values of the explanatory variables (or predictors) is assumed to be an affine function of those values; less commonly, the conditional median or some other quantile is used. Like all forms of regression analysis, linear regression focuses on the conditional probability distribution of the response given the values of the predictors, rather than on the joint probability distribution of all of these variables, which is the domain of multivariate analysis.
Linear regression was the first type of regression analysis to be studied rigorously, and to be used extensively in practical applications. This is because models which depend linearly on their unknown parameters are easier to fit than models which are non-linearly related to their parameters and because the statistical properties of the resulting estimators are easier to determine.
Linear regression has many practical uses. Most applications fall into one of the following two broad categories:
- If the goal is prediction, or forecasting, or error reduction, linear regression can be used to fit a predictive model to an observed data set of values of the response and explanatory variables. After developing such a model, if additional values of the explanatory variables are collected without an accompanying response value, the fitted model can be used to make a prediction of the response.
- If the goal is to explain variation in the response variable that can be attributed to variation in the explanatory variables, linear regression analysis can be applied to quantify the strength of the relationship between the response and the explanatory variables, and in particular to determine whether some explanatory variables may have no linear relationship with the response at all, or to identify which subsets of explanatory variables may contain redundant information about the response.
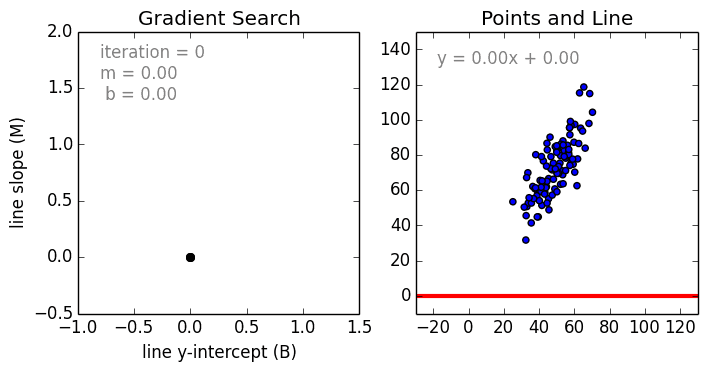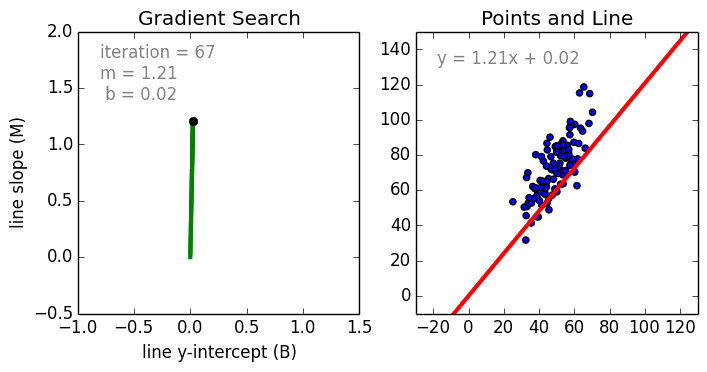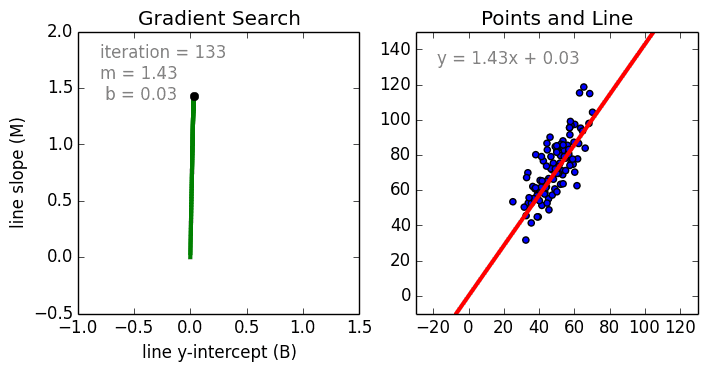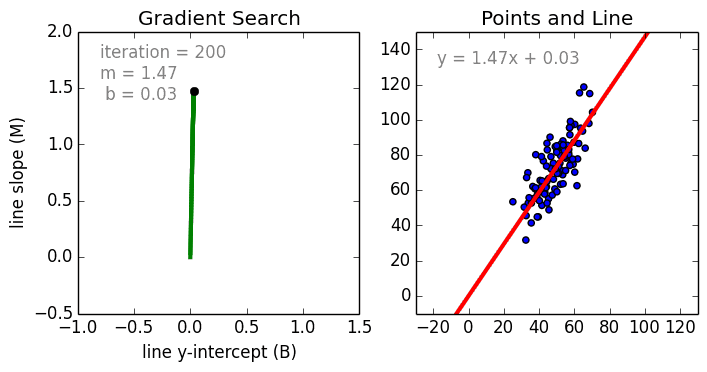
Linear regression models are often fitted using the least squares approach, but they may also be fitted in other ways, such as by minimizing the "lack of fit" in some other norm (as with least absolute deviations regression), or by minimizing a penalized version of the least squares cost function as in ridge regression (L2-norm penalty) and lasso (L1-norm penalty). Conversely, the least squares approach can be used to fit models that are not linear models. Thus, although the terms "least squares" and "linear model" are closely linked, they are not synonymous.
